Palmistry and Palm Readers: Difference between revisions
(grrr) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
=='''IMPORTANT NOTICE:'''== | |||
This is a site devoted to HISTORICAL IMAGES AND TEXTS. If you are triggered by words used to describe people in the past or by seeing cartoon images drawn in the past, please leave this site now. It is for HISTORIANS and not for you. | |||
== Your Fate is in Your Hands == | == Your Fate is in Your Hands == | ||
As a form of [[Defining Divination|divination]], palmistry combines [[Defining Divination|character analysis]] with [[Defining Divination|fortune telling]]. Most readers consider it to be one of the more scientific forms of prediction, because a great many of the features of the hand are determined by genetics, including the presence of congenital diseases and the likelihood of the sitter following a career that an ancestor also pursued. | |||
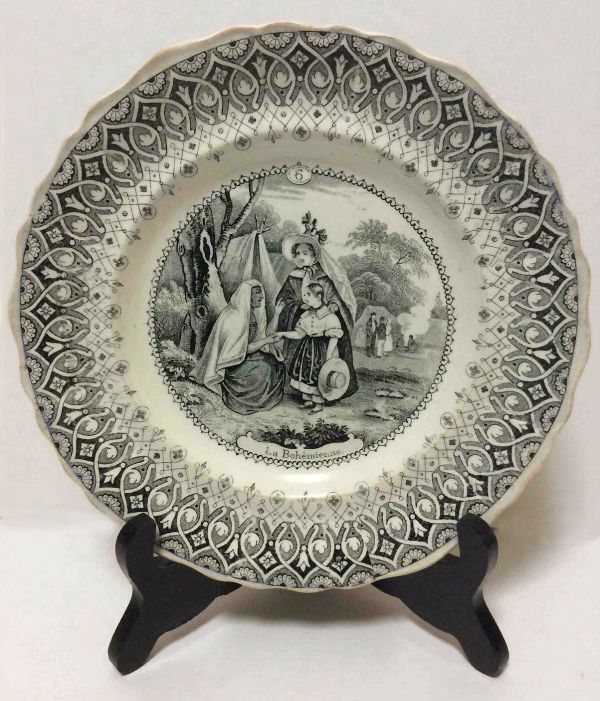
[[File:Creil-Montereau-Leboeuf-1834-La-Bohemian-Fortune-Telling-1.jpg|center|thumb|600px|A Crell, Monterau, and Leboeuf transferware soup plate from 1834 titled "La Bohémienne," which depicts a Bohemian Romani woman beside her tent reading the palm of a little French girl as her mother looks on with slight alarm.]] | [[File:Creil-Montereau-Leboeuf-1834-La-Bohemian-Fortune-Telling-1.jpg|center|thumb|600px|A Crell, Monterau, and Leboeuf transferware soup plate from 1834 titled "La Bohémienne," which depicts a Bohemian Romani woman beside her tent reading the palm of a little French girl as her mother looks on with slight alarm.]] | ||
As far as i can tell, the scientific study of palm reading began or became widely popular in India, centuries ago. It travelled to Europe with the Romani people, who date their movement Westward to the time of Alexander the Great, and still maintain many Indian customs and beliefs. | As far as i can tell, the scientific study of palm reading began or became widely popular in India, centuries ago. It travelled to Europe with the Romani people, who date their movement Westward to the time of Alexander the Great, and still maintain many Indian customs and beliefs. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 44: | ||
Some of the first experiences Americans and Europeans had with palmistry as a form of character analysis or fortune telling was with Romani women who read their hands. In the 19th century, the Romani were forbidden to set up shops or permanent dwellings, and lived in camps outside of towns, coming in to trade at the markets during feast days, market days, and fairs. The bolder seekers after fortunes would ride or walk out to the "Gypsy camp" to have their futures told. | Some of the first experiences Americans and Europeans had with palmistry as a form of character analysis or fortune telling was with Romani women who read their hands. In the 19th century, the Romani were forbidden to set up shops or permanent dwellings, and lived in camps outside of towns, coming in to trade at the markets during feast days, market days, and fairs. The bolder seekers after fortunes would ride or walk out to the "Gypsy camp" to have their futures told. | ||
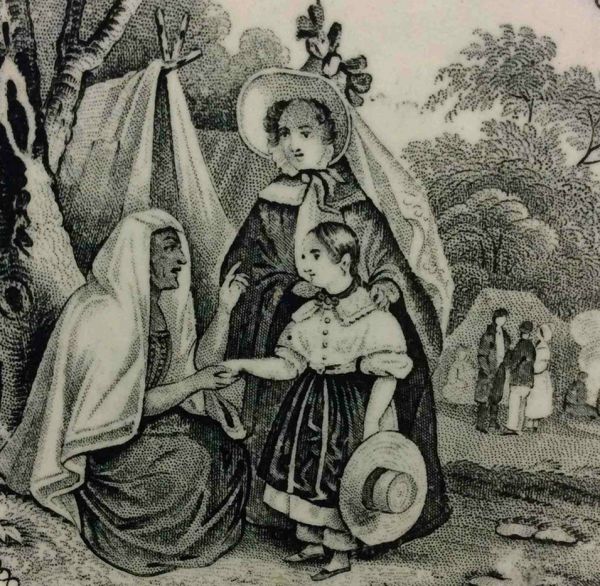
[[File:Creil-Montereau-Leboeuf-1834-La-Bohemian-Fortune-Telling-Close-Up.jpg|center|thumb|600px|Central detail of the Crell, Monterau, and Leboeuf transferware soup plate from 1834 titled "La Bohémienne." The look of surpise or shock on the mother's face is typical of the stereotype. | |||
]] | [[File:Creil-Montereau-Leboeuf-1834-La-Bohemian-Fortune-Telling-Close-Up.jpg|center|thumb|600px|Central detail of the Crell, Monterau, and Leboeuf transferware soup plate from 1834 titled "La Bohémienne." The look of surpise or shock on the mother's face is typical of the stereotype. ]] | ||
The image of the uncanny, nomadic, frightening "Gypsy woman" who reads the hand and makes dire predictions reached a height in Britain and America during the late Victorian era and continued well on into the 20th century. A common topic for postcards, the image was usually that of a young Anglo woman having her hand read by an old Romani woman, out of doors, either amidst ruins or near a campsite. | The image of the uncanny, nomadic, frightening "Gypsy woman" who reads the hand and makes dire predictions reached a height in Britain and America during the late Victorian era and continued well on into the 20th century. A common topic for postcards, the image was usually that of a young Anglo woman having her hand read by an old Romani woman, out of doors, either amidst ruins or near a campsite. | ||
[[File:Gipsys-Warning-Valentines-Series-Palmistry.jpg|center|600px|thumb|"The Gipsy's Warning," a tinted photographic postcard published circa 1910.]] | [[File:Gipsys-Warning-Valentines-Series-Palmistry.jpg|center|600px|thumb|"The Gipsy's Warning," a tinted photographic postcard published circa 1910.]] | ||
In time, the elderly Romani woman began to fuse with the English and American stereotype of "the witch," a hook-nosed woman who wore clothes similar to Welsh villagers and who was thought to have evil intentions toward more culturally normative women. The "gypsy witch" competed with the "Bohemian gypsy" as a stereotype for decades. For example, "Gypsy Witch" brand oracle cards became popular in the early 20th century, and they are still in print to this day. | In time, the elderly Romani woman began to fuse with the English and American stereotype of "the witch," a hook-nosed woman who wore clothes similar to Welsh villagers and who was thought to have evil intentions toward more culturally normative women. The "gypsy witch" competed with the "Bohemian gypsy" as a stereotype for decades. For example, "Gypsy Witch" brand oracle cards became popular in the early 20th century, and they are still in print to this day. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 61: | ||
In time, the word "gypsy" also came to simply mean "nomadic," or "a traveller." The Irish Travellers were and are hereditary families who drive about the countryside in caravans and may work at odd jobs. "Gypsy" was also a term applied to carnival, vaudeville, and fair workers, who moved from town to town while earning money by providing entertainment in small venues. Gypsy Rose Lee, for instance, was the stage name of Rose Louise Hovick (1911–1970), a non-Roma who worked in on the burlesque circuit as a striptease artist and became well-known as an actress, author, and playwright whose 1957 memoir became a 1959 stage musical title "Gypsy." | In time, the word "gypsy" also came to simply mean "nomadic," or "a traveller." The Irish Travellers were and are hereditary families who drive about the countryside in caravans and may work at odd jobs. "Gypsy" was also a term applied to carnival, vaudeville, and fair workers, who moved from town to town while earning money by providing entertainment in small venues. Gypsy Rose Lee, for instance, was the stage name of Rose Louise Hovick (1911–1970), a non-Roma who worked in on the burlesque circuit as a striptease artist and became well-known as an actress, author, and playwright whose 1957 memoir became a 1959 stage musical title "Gypsy." | ||
[[File:Book-Illo-Palmistry-Fortune-Telling-By-F-D-Bedford-c-1920.jpg|thumb|600px|center|"Fortune Telling," a book illustration by F. D. Bedford, circa 1920, in which the travelling "gypsy witch" has left the outdoors domain of the Bohemian Romani and intrudes into the domestic kitchen of those to whom she issues her frightening prophesies. The clothing, 19th century in style, informs us that the artist conceived this as a scene from the romantic past.]] | [[File:Book-Illo-Palmistry-Fortune-Telling-By-F-D-Bedford-c-1920.jpg|thumb|600px|center|"Fortune Telling," a book illustration by F. D. Bedford, circa 1920, in which the travelling "gypsy witch" has left the outdoors domain of the Bohemian Romani and intrudes into the domestic kitchen of those to whom she issues her frightening prophesies. The clothing, 19th century in style, informs us that the artist conceived this as a scene from the romantic past.]] | ||
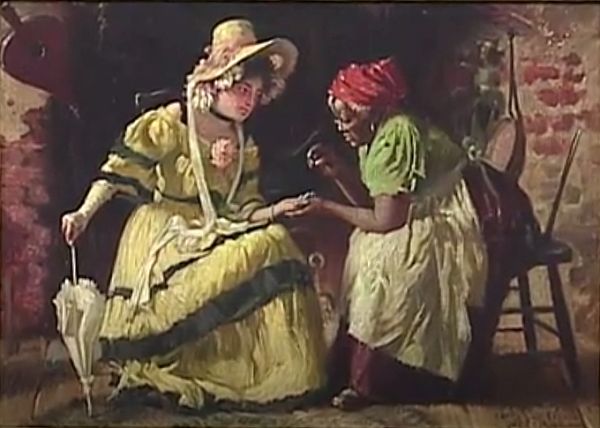
Despite the stereotypes surrounding palmistry as the inherently fraudulent but weirdly accurate mutterings of old Romani women, palmistry itself, as a form of reading, gained much popularity in America and England around the beginning of the 20th century. The artist Harry Roseland, who documented the life of a professional African-American fortune teller in New York City from the 1890s through the 1920s, painted her as a cartomancer, tea leaf reader, crystal scryer, and palmist. In keeping with the theme of the reader as outside mainstream culture, her client was a sweet young Anglo-Saxon woman, but because Roseland sought to uplift the kindliness and normality of the black reader, the scene is homey and domestic, and the title of the picture is "Good Luck, Honey." | Despite the stereotypes surrounding palmistry as the inherently fraudulent but weirdly accurate mutterings of old Romani women, palmistry itself, as a form of reading, gained much popularity in America and England around the beginning of the 20th century. The artist Harry Roseland, who documented the life of a professional African-American fortune teller in New York City from the 1890s through the 1920s, painted her as a cartomancer, tea leaf reader, crystal scryer, and palmist. In keeping with the theme of the reader as outside mainstream culture, her client was a sweet young Anglo-Saxon woman, but because Roseland sought to uplift the kindliness and normality of the black reader, the scene is homey and domestic, and the title of the picture is "Good Luck, Honey." | ||
| Line 64: | Line 71: | ||
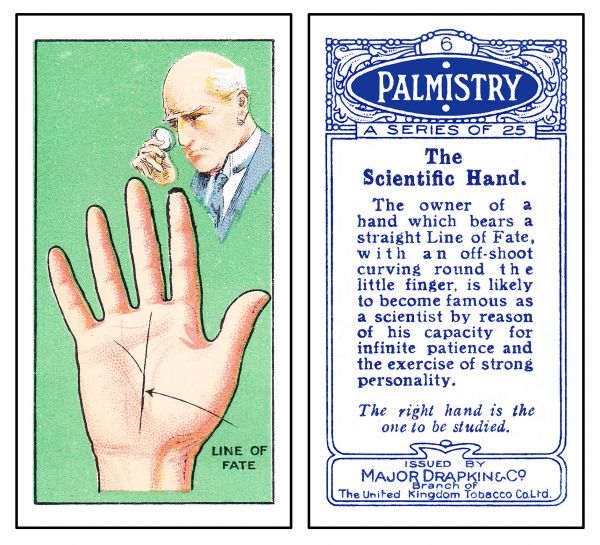
Around this time terms like "scientific palmistry" and "medical palmistry" began to be applied to palm reading, in keeping with its obvious connections to physical traits. The "scientific palmistry" systems derived from Indian teachers, not from the wandering Bohemian Romani. Scientific palm readers were known for their accuracy, and because of them palmistry became extremely popular in Europe and North America. Common people of all walks of life, both male and female, sought to learn how to read the hand. Instruction books and flash cards were easy to find. | Around this time terms like "scientific palmistry" and "medical palmistry" began to be applied to palm reading, in keeping with its obvious connections to physical traits. The "scientific palmistry" systems derived from Indian teachers, not from the wandering Bohemian Romani. Scientific palm readers were known for their accuracy, and because of them palmistry became extremely popular in Europe and North America. Common people of all walks of life, both male and female, sought to learn how to read the hand. Instruction books and flash cards were easy to find. | ||
[[File: Major-Drapkin-Palmistry-Card-06.jpg|thumb|600px|center|One of 25 instructional Palmistry cigarette cards published in 1927 by the Major Drapkin & Co. Branch of The United Kingdom Tobacco Co. Ltd.]] | [[File: Major-Drapkin-Palmistry-Card-06.jpg|thumb|600px|center|One of 25 instructional Palmistry cigarette cards published in 1927 by the Major Drapkin & Co. Branch of The United Kingdom Tobacco Co. Ltd.]] | ||
By the 1940s, palmistry was well accepted in America. It was so much a part of American life that it was even used as a theme in institutional magazine advertisements. For instance, this ad for the National Dairy Products Corporation links the Romani reader — now a kindly young woman of maternal mien -- with the word "scientific," as the mother has her little girl's hand read, and only good things are foretold. The tattered, rural campsite of La Bohemiénne is now a striped carnival tent at a county fair, and although the reader still shows a bit of exoticism by letting her blouse fall off her shoulder, the mother, mostly cropped out of the photo, wears a smart woolen suit and probably approves of the divination. | By the 1940s, palmistry was well accepted in America. It was so much a part of American life that it was even used as a theme in institutional magazine advertisements. For instance, this ad for the National Dairy Products Corporation links the Romani reader — now a kindly young woman of maternal mien -- with the word "scientific," as the mother has her little girl's hand read, and only good things are foretold. The tattered, rural campsite of La Bohemiénne is now a striped carnival tent at a county fair, and although the reader still shows a bit of exoticism by letting her blouse fall off her shoulder, the mother, mostly cropped out of the photo, wears a smart woolen suit and probably approves of the divination. | ||
[[File:Have-Your-Fortune-Told-Palmistry-National-Dairy-Products-Ad-cleaned-smaller.jpg|600px|center|thumb|1940s magazine ad for the National Dairy Products Corporation, featuring a domesticated palm reader. The small cut-line "Buy War Bonds and Stamps" under the photo dates it to the years 1941-1945, during the Second World War.]] | [[File:Have-Your-Fortune-Told-Palmistry-National-Dairy-Products-Ad-cleaned-smaller.jpg|600px|center|thumb|1940s magazine ad for the National Dairy Products Corporation, featuring a domesticated palm reader. The small cut-line "Buy War Bonds and Stamps" under the photo dates it to the years 1941-1945, during the Second World War.]] | ||
Meanwhile, in India, the land where palmistry originated, with no negative or exotic stereotypes to confront and overcome, palmistry persisted as a well-known and culturally approved form of character analysis and prognostication. | Meanwhile, in India, the land where palmistry originated, with no negative or exotic stereotypes to confront and overcome, palmistry persisted as a well-known and culturally approved form of character analysis and prognostication. | ||
This four-page flyer, printed in Bombay (now Mumbai), India, in 1940, shows how respectable and normal palm reading was in India, at a time when American palm readers often were treated as outsiders and frauds. | This four-page flyer, printed in Bombay (now Mumbai), India, in 1940, shows how respectable and normal palm reading was in India, at a time when American palm readers often were treated as outsiders and frauds. | ||
[[File:bashir-ba-palmistry-flyer-page-1-smaller.jpg|center|600px|thumb|Page 1 of the 1940 advertising flyer for Bashir, B.A., a scientific Indian palmist located in Bombay (now Mumbai), India.]] | [[File:bashir-ba-palmistry-flyer-page-1-smaller.jpg|center|600px|thumb|Page 1 of the 1940 advertising flyer for Bashir, B.A., a scientific Indian palmist located in Bombay (now Mumbai), India.]] | ||
| Line 82: | Line 94: | ||
[[File:bashir-ba-palmistry-flyer-page-4-smaller.jpg|center|600px|thumb|Page 4 of the 1940 advertising flyer for Bashir, B.A., featuring a newspaper account and a testimonial from a doctor. The terms "Zamindar" and "Jagirdar" on this page refer to an autocratic land-owning class established in the 13th century under Muslim rule, similar to European feudal lords. The Jagirdar system continued under British colonial rule, but in 1951, after Indian independence and the partition of Pakistan and Bangladesh, it was abolished.]] | [[File:bashir-ba-palmistry-flyer-page-4-smaller.jpg|center|600px|thumb|Page 4 of the 1940 advertising flyer for Bashir, B.A., featuring a newspaper account and a testimonial from a doctor. The terms "Zamindar" and "Jagirdar" on this page refer to an autocratic land-owning class established in the 13th century under Muslim rule, similar to European feudal lords. The Jagirdar system continued under British colonial rule, but in 1951, after Indian independence and the partition of Pakistan and Bangladesh, it was abolished.]] | ||
By the time that genetics entered the palmistry picture in the late 20th century, the concepts of "scientific palmistry" and "medical palmistry" were finally accepted, and the idea that palm reading, a much-maligned form of folkloric fortune telling, had held and preserved so many interesting genetic markers served to remove some of the stigma from its traditional practice in Europe and America. | By the time that genetics entered the palmistry picture in the late 20th century, the concepts of "scientific palmistry" and "medical palmistry" were finally accepted, and the idea that palm reading, a much-maligned form of folkloric fortune telling, had held and preserved so many interesting genetic markers served to remove some of the stigma from its traditional practice in Europe and America. | ||
By the early 21st century, it had became a popular opinion that the word "gypsy" ("Egyptian") was a deliberate "racial slur" directed against Romani people, who are of Indian heritage. For this reason, web pages such as this one must now carry notices, trigger warnings, and lengthy explanations of the many and diverse meanings of the word "gypsy." | |||
==See Also == | ==See Also == | ||
Revision as of 02:25, 9 August 2023
In this installment of "Your Wate and Fate," we take a sneak-peek look at an upcoming page that will eventually be on display to the public. As a Patreon supporter, you have access to the page one full year before the public does.
- Patreon Release Date: September 14th, 2021
- Public Release Date: September 14th, 2022.
Please tell your friends that they can subscribe to my Patreon stream for $2.00 per week:
Patrons; To discuss this and other Patreon pages with me, join my private Patreon Forum:
Support Your Wate and Fate
All of the material you have access to here -- the instructive booklets, the nostalgic postcards, the boldly graphic ephemera, and all of the historical information researched and shared from the mind of the woman who is making it all happen -- can easily fit into one 8 x 10 foot room in an old Victorian farmhouse, but you would never see it without the investment of the time it takes to produce such a site and the caloric input such a site requires in the form of food for the writer, graphic designer, and database manager, as well as the US currency needed to pay for the computers, software applications, scanners, electricity, and internet connectivity that bring it out of that little room and into the world.
So, as you can see, this site is the darling of many, and it is growing at a rapid rate ... but although it is "free," there also is a cost. The financial support of my Patreon subscribers -- my Patrons -- underwrites this cost.
IMPORTANT NOTICE:
This is a site devoted to HISTORICAL IMAGES AND TEXTS. If you are triggered by words used to describe people in the past or by seeing cartoon images drawn in the past, please leave this site now. It is for HISTORIANS and not for you.
Your Fate is in Your Hands
As a form of divination, palmistry combines character analysis with fortune telling. Most readers consider it to be one of the more scientific forms of prediction, because a great many of the features of the hand are determined by genetics, including the presence of congenital diseases and the likelihood of the sitter following a career that an ancestor also pursued.
As far as i can tell, the scientific study of palm reading began or became widely popular in India, centuries ago. It travelled to Europe with the Romani people, who date their movement Westward to the time of Alexander the Great, and still maintain many Indian customs and beliefs.
Hand reading was soon associated with Romani practitioners in Eastern Europe. As these people, wrongly called "Gypsies" by Europeans who thought that they had come from Egypt, moved Westward into Europe and Great Britain, they actually brought two popular forms of fortune telling with them — palm reading and fortune telling with birds. Both of these were practiced in public, by women, the Romani men being mostly horse trainers, dealers, and brokers, a hereditary trade in their culture, and a vital part of their nomadic lifestyle. That nomadic life, which led to their unaccountability to local authorities, also led to discrimination against the Romani, and an othering of their way of life. Words like mysterious, exotic, strange, and weird were attached to them.
Eventually, because so many settled in the region then known as Bohemia (now the Czech Republic), they came to be known as Bohemians, a word that, in turn, came to mean anyone, from any culture or region, who chooses to live outside of society's conventional norms. The Bohemian lifestyle was one of freedom, eccentricity, and reduced accountability to the capitalist state. These days the derivative fashion term Boho refers to garments that are free flowing, with long skirts and full sleeves, resembling the clothes of the 19th century Romani in Bohemia.
Some of the first experiences Americans and Europeans had with palmistry as a form of character analysis or fortune telling was with Romani women who read their hands. In the 19th century, the Romani were forbidden to set up shops or permanent dwellings, and lived in camps outside of towns, coming in to trade at the markets during feast days, market days, and fairs. The bolder seekers after fortunes would ride or walk out to the "Gypsy camp" to have their futures told.
The image of the uncanny, nomadic, frightening "Gypsy woman" who reads the hand and makes dire predictions reached a height in Britain and America during the late Victorian era and continued well on into the 20th century. A common topic for postcards, the image was usually that of a young Anglo woman having her hand read by an old Romani woman, out of doors, either amidst ruins or near a campsite.
In time, the elderly Romani woman began to fuse with the English and American stereotype of "the witch," a hook-nosed woman who wore clothes similar to Welsh villagers and who was thought to have evil intentions toward more culturally normative women. The "gypsy witch" competed with the "Bohemian gypsy" as a stereotype for decades. For example, "Gypsy Witch" brand oracle cards became popular in the early 20th century, and they are still in print to this day.
At the beginning of the 20th century, when crystal balls became very popular among Spiritualists, spirit mediums, and fortune tellers, the image of the "gypsy" holding a crystal ball -- and often most definitely NOT a Roma woman! -- was added to the palmistry and card-reader as a stereotype, and found in many forms of commercial art.
Another word for "gypsy," in the sense of a Roma person, is Tzigane (French) or Zigeuner (Gernam). By the end of the 19th century and well into the 20th century, this word was applied to everything from perfumes to oracle cards. Tzigane by Corday of Paris was a pefrume advertised as being "for the Gypsy in your soul" and Zigeuner Wahrsagekarten ("Gypsy Fortune Telling Cards") were made by Piatnik of Vienna) -- and neither specifically caried images of Roma people.
In time, the word "gypsy" also came to simply mean "nomadic," or "a traveller." The Irish Travellers were and are hereditary families who drive about the countryside in caravans and may work at odd jobs. "Gypsy" was also a term applied to carnival, vaudeville, and fair workers, who moved from town to town while earning money by providing entertainment in small venues. Gypsy Rose Lee, for instance, was the stage name of Rose Louise Hovick (1911–1970), a non-Roma who worked in on the burlesque circuit as a striptease artist and became well-known as an actress, author, and playwright whose 1957 memoir became a 1959 stage musical title "Gypsy."

Despite the stereotypes surrounding palmistry as the inherently fraudulent but weirdly accurate mutterings of old Romani women, palmistry itself, as a form of reading, gained much popularity in America and England around the beginning of the 20th century. The artist Harry Roseland, who documented the life of a professional African-American fortune teller in New York City from the 1890s through the 1920s, painted her as a cartomancer, tea leaf reader, crystal scryer, and palmist. In keeping with the theme of the reader as outside mainstream culture, her client was a sweet young Anglo-Saxon woman, but because Roseland sought to uplift the kindliness and normality of the black reader, the scene is homey and domestic, and the title of the picture is "Good Luck, Honey."

Around this time terms like "scientific palmistry" and "medical palmistry" began to be applied to palm reading, in keeping with its obvious connections to physical traits. The "scientific palmistry" systems derived from Indian teachers, not from the wandering Bohemian Romani. Scientific palm readers were known for their accuracy, and because of them palmistry became extremely popular in Europe and North America. Common people of all walks of life, both male and female, sought to learn how to read the hand. Instruction books and flash cards were easy to find.
By the 1940s, palmistry was well accepted in America. It was so much a part of American life that it was even used as a theme in institutional magazine advertisements. For instance, this ad for the National Dairy Products Corporation links the Romani reader — now a kindly young woman of maternal mien -- with the word "scientific," as the mother has her little girl's hand read, and only good things are foretold. The tattered, rural campsite of La Bohemiénne is now a striped carnival tent at a county fair, and although the reader still shows a bit of exoticism by letting her blouse fall off her shoulder, the mother, mostly cropped out of the photo, wears a smart woolen suit and probably approves of the divination.
Meanwhile, in India, the land where palmistry originated, with no negative or exotic stereotypes to confront and overcome, palmistry persisted as a well-known and culturally approved form of character analysis and prognostication.
This four-page flyer, printed in Bombay (now Mumbai), India, in 1940, shows how respectable and normal palm reading was in India, at a time when American palm readers often were treated as outsiders and frauds.

By the time that genetics entered the palmistry picture in the late 20th century, the concepts of "scientific palmistry" and "medical palmistry" were finally accepted, and the idea that palm reading, a much-maligned form of folkloric fortune telling, had held and preserved so many interesting genetic markers served to remove some of the stigma from its traditional practice in Europe and America.
By the early 21st century, it had became a popular opinion that the word "gypsy" ("Egyptian") was a deliberate "racial slur" directed against Romani people, who are of Indian heritage. For this reason, web pages such as this one must now carry notices, trigger warnings, and lengthy explanations of the many and diverse meanings of the word "gypsy."
See Also
Thanks to nagasiva yronwode, my own King of Hearts, for helping with image acquisition and clean-up for this page.
catherine yronwode
curator, historian, and docent
Your Wate and fate